Experimental Farm (Kebun Percobaan)
Overview
The Experimental Farm of the Agrotechnology Study Programme serves as an open learning platform and research hub for students, lecturers, and external partners. This facility integrates conventional agricultural practices with modern smart-farming technologies to support education, research, and community service.
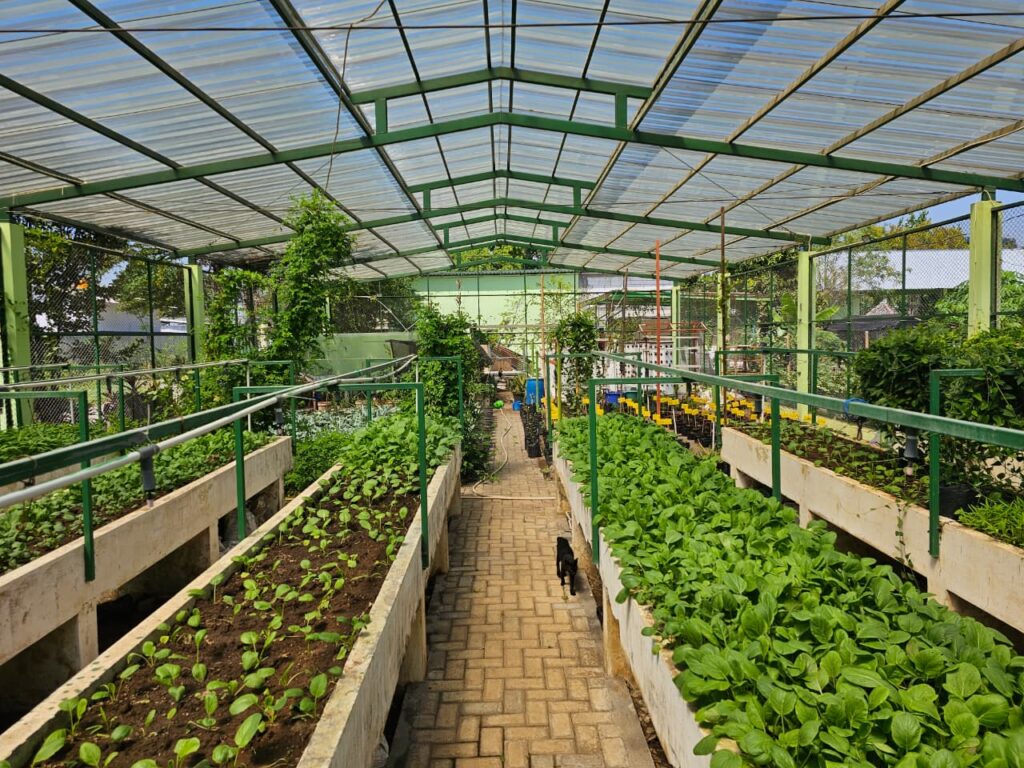


Experimental Farm

Head of Experimental Farm

Fitri Wijayanti, S.P., M.P.
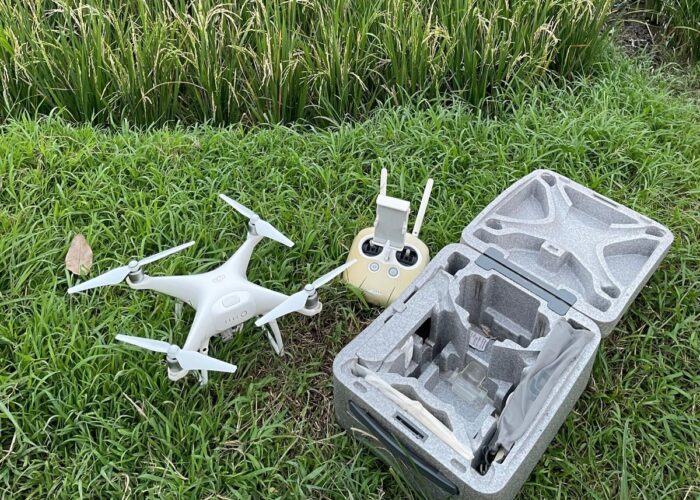
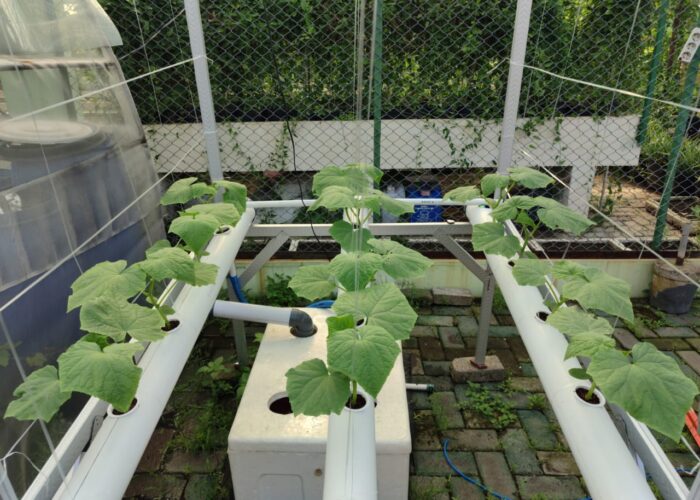
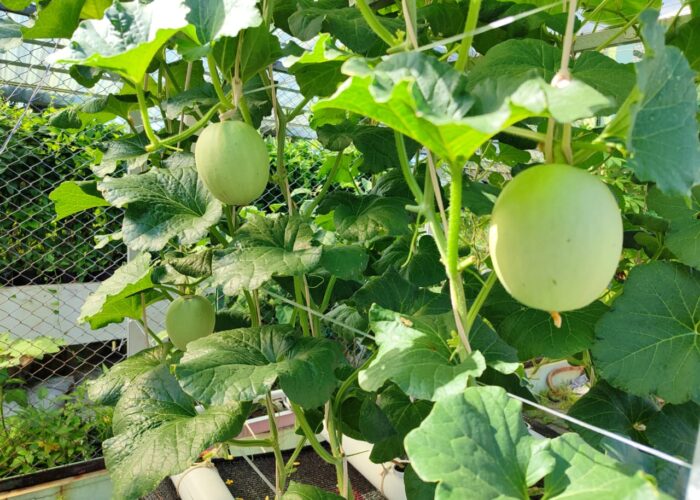
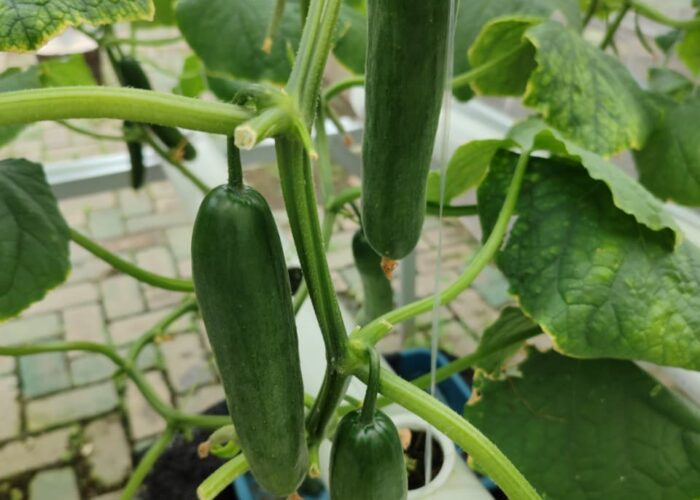
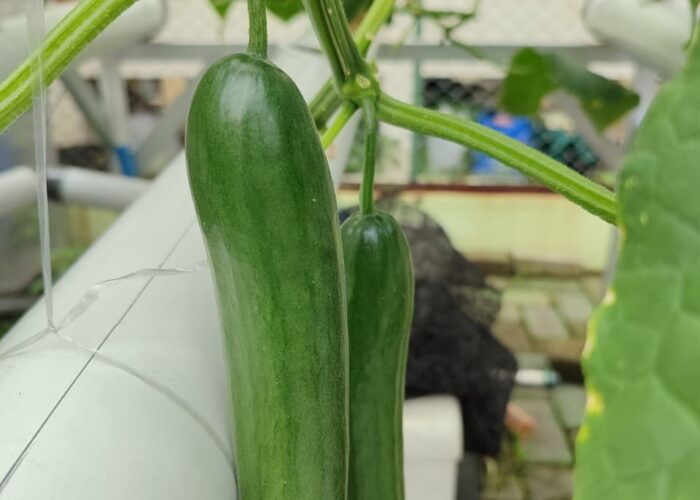








Facilities The Experimental Farm is equipped with:
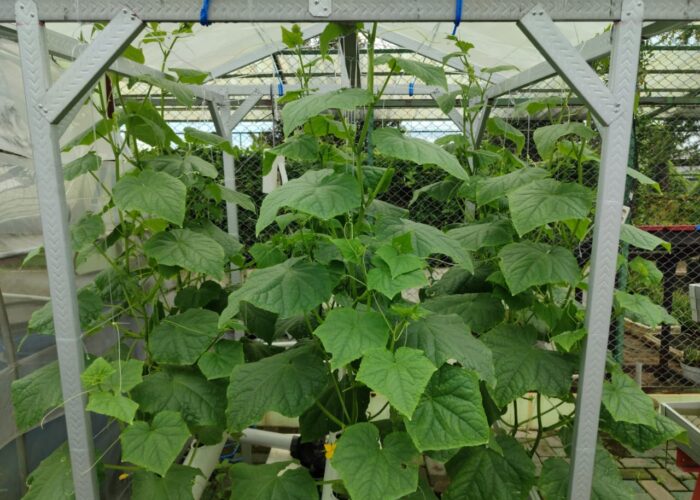
- 7 Smart Greenhouses with IoT Technology (temperature, humidity, and irrigation sensors).
- Agricultural Drone for precision farming, mapping, and monitoring.
- Biomass Chopper Machine and Granulator Machine for organic fertilizer production.
- Fermentor Machine for biofertilizer and biopesticide development.
- Hydroponic Installations for urban farming practices.
- Sprinkler Irrigation System and Water Pumps for efficient water management.
- Drones are revolutionizing experimental agriculture by making research faster, smarter, and more precise. With high-resolution cameras and advanced sensors, drones capture valuable data on crop health, soil conditions, and growth patterns in real time. From monitoring trials to mapping fields and even applying inputs with pinpoint accuracy, drones reduce labor costs while improving the reliability of results. For researchers and innovators, this means quicker insights, stronger data, and sustainable solutions for the future of farming.
- Greenhouses play a vital role in experimental agriculture by providing a controlled environment where crops can be studied without the uncertainties of outdoor conditions. They allow researchers to manage variables such as temperature, light, water, and soil, making it possible to conduct reliable trials across different seasons and treatments. Smart greenhouses take this concept further by integrating sensors, automation, and digital monitoring systems. These technologies enable real-time control of climate, irrigation, and nutrient delivery, ensuring precision and consistency in every experiment. Data collected from smart greenhouses helps researchers analyze plant responses more accurately, optimize resources, and accelerate the development of sustainable farming practices. Together, traditional and smart greenhouses form the foundation of modern agricultural research—combining protection, precision, and innovation to create solutions for the future of food security
- Greenhouses play a vital role in experimental agriculture by providing a controlled environment where crops can be studied without the uncertainties of outdoor conditions. They allow researchers to manage variables such as temperature, light, water, and soil, making it possible to conduct reliable trials across different seasons and treatments. Smart greenhouses take this concept further by integrating sensors, automation, and digital monitoring systems. These technologies enable real-time control of climate, irrigation, and nutrient delivery, ensuring precision and consistency in every experiment. Data collected from smart greenhouses helps researchers analyze plant responses more accurately, optimize resources, and accelerate the development of sustainable farming practices. Together, traditional and smart greenhouses form the foundation of modern agricultural research—combining protection, precision, and innovation to create solutions for the future of food security
- Experimental fields serve as living laboratories where research meets real-world farming. By testing crop varieties, soil treatments, and sustainable practices directly in the field, we generate practical solutions that can be applied to strengthen food security and improve agricultural productivity.
- Smart irrigation brings precision to farming by using sensors and automation to deliver the right water at the right time. It saves resources, boosts crop health, and supports sustainable agriculture through efficient water management.
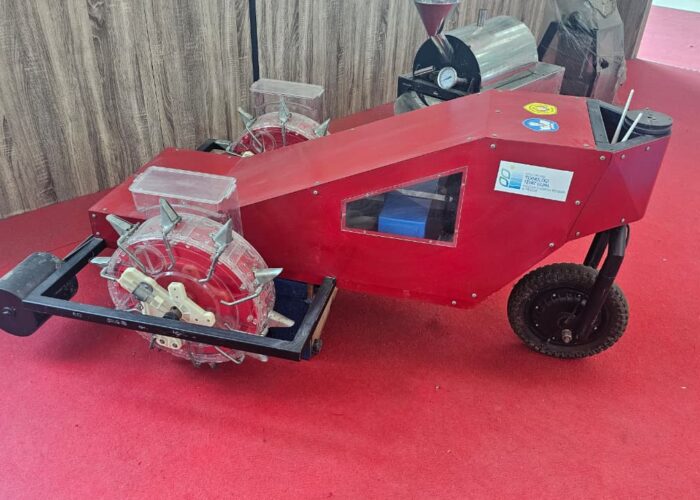
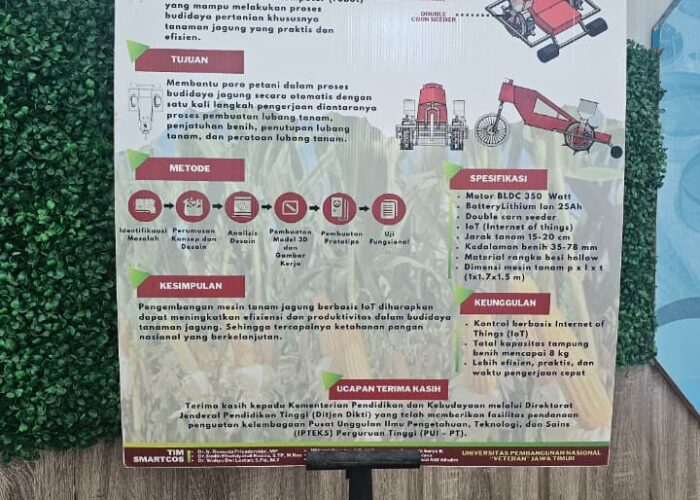
- Smart planters use sensors and automation to place seeds with precision, ensuring optimal depth, spacing, and growth. This technology boosts efficiency, reduces waste, and supports sustainable farming while providing reliable results for agricultural research.
Academic and Research Functions:
Facilities The Experimental Farm is equipped with:
- Practical field classes for Crop Cultivation, Agroforestry, Sustainable Agriculture, and Precision Agriculture.
- Student research projects on smart agriculture, soil-water management, biofertilizer application, and pest control.
- Supporting capstone projects and thesis research related to agrotechnology innovation.
- Pilot site for community service and training programmes (urban farming, sustainable agriculture, digital farming).
Partnership and Collaboration The Experimental Farm is open for collaboration with:
- Universities (joint research, student exchange, collaborative field experiments).
- Companies (technology testing, product development, field trials).
- Government and Communities (capacity building, farmer training, green village initiatives).






